-
🤖 Alan Turing (1912-1954)

Turing Machine (1936), Turing Test (1950)
Alan Turing thought of a machine that could solve any problem a computer can if it had the right instructions. He also came up with a test to see if a computer could pretend to be human.
- Language Skills: The machine should understand and respond naturally and appropriately.
- Thinking and Solving: The machine should solve problems and think logically like a human.
- Creativity: The machine should create new and original ideas.
- Emotions: The machine should recognize and respond to emotions.
- Learning: The machine should know a lot and learn from new experiences.
-
☎️ Claude Shannon (1916-2001)

Information Theory (1948)
Claude Shannon's work made it possible for us to send and store data efficiently. While working for Bell Labs on their telephone network, he designed and implemented a complete digital encoding technique. Think about texting or watching videos online - that's thanks to his ideas!
-
⏰ John McCarthy (1927-2011)

John McCarthy is the person who came up with the term "Artificial Intelligence" (in 1956) and invented a programming language (lisp) that helped researchers develop AI.
John also initiated the development of time-sharing systems to fairly share expensive computing resources. These practices are now the foundations of the cloud computing industry.
-
1980s - Computers Get More Human
-
1990s - AI Begins to Compete
-
2010s - Real-Time Computer Vision
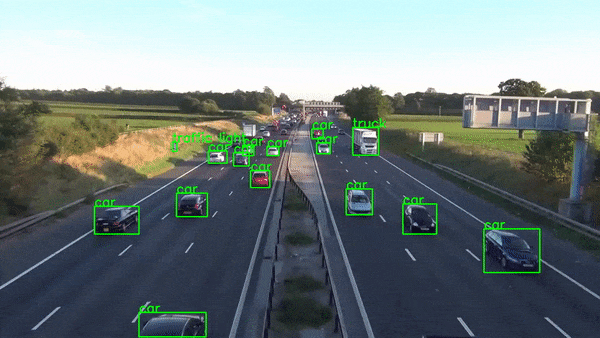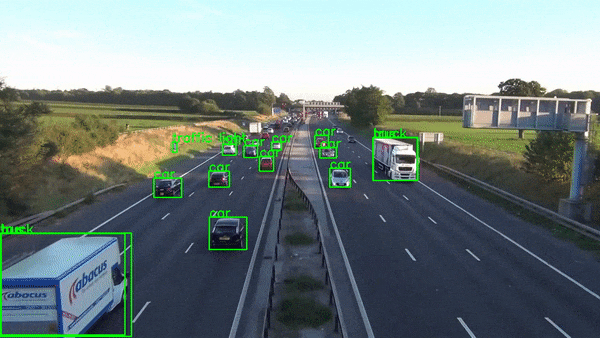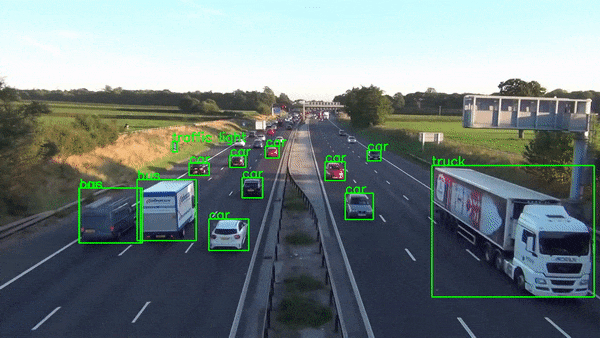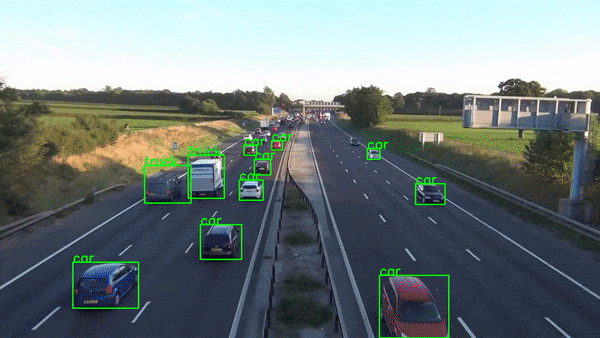
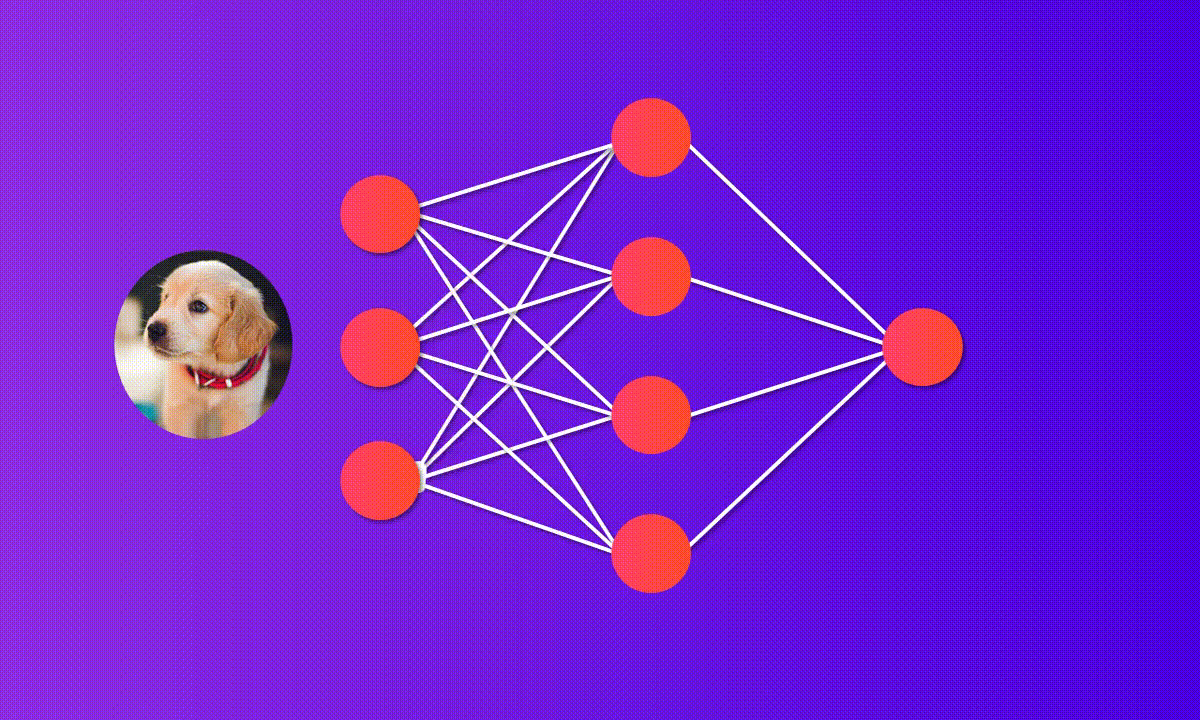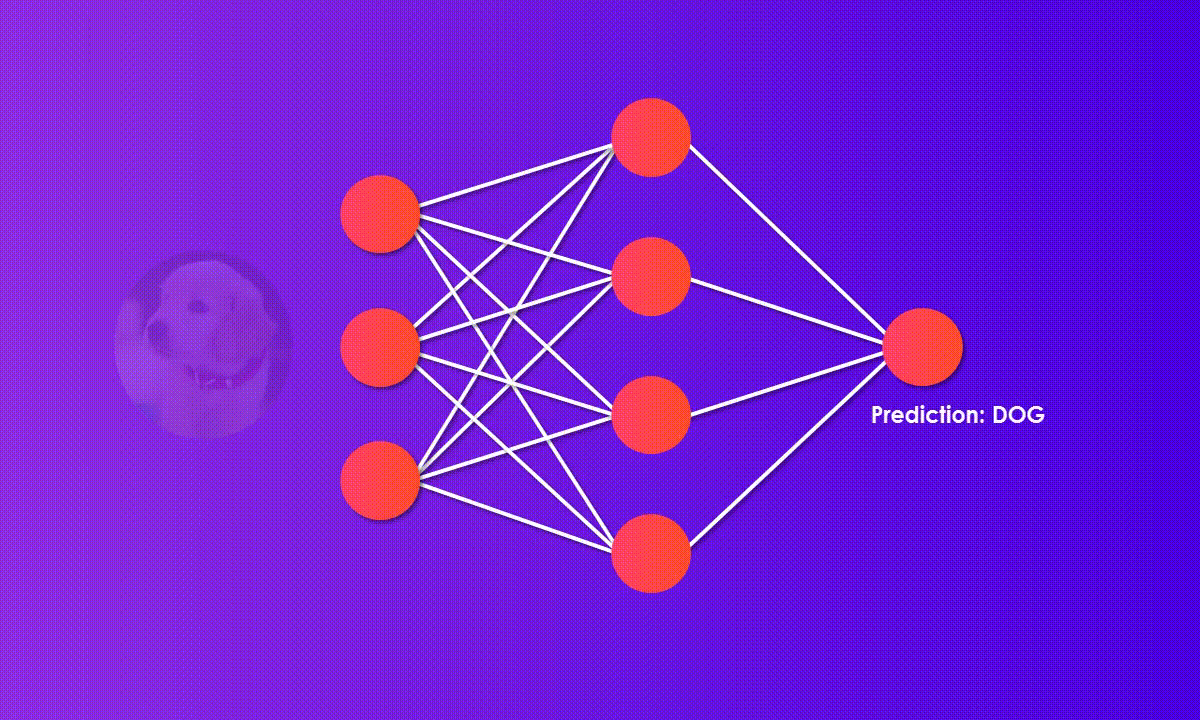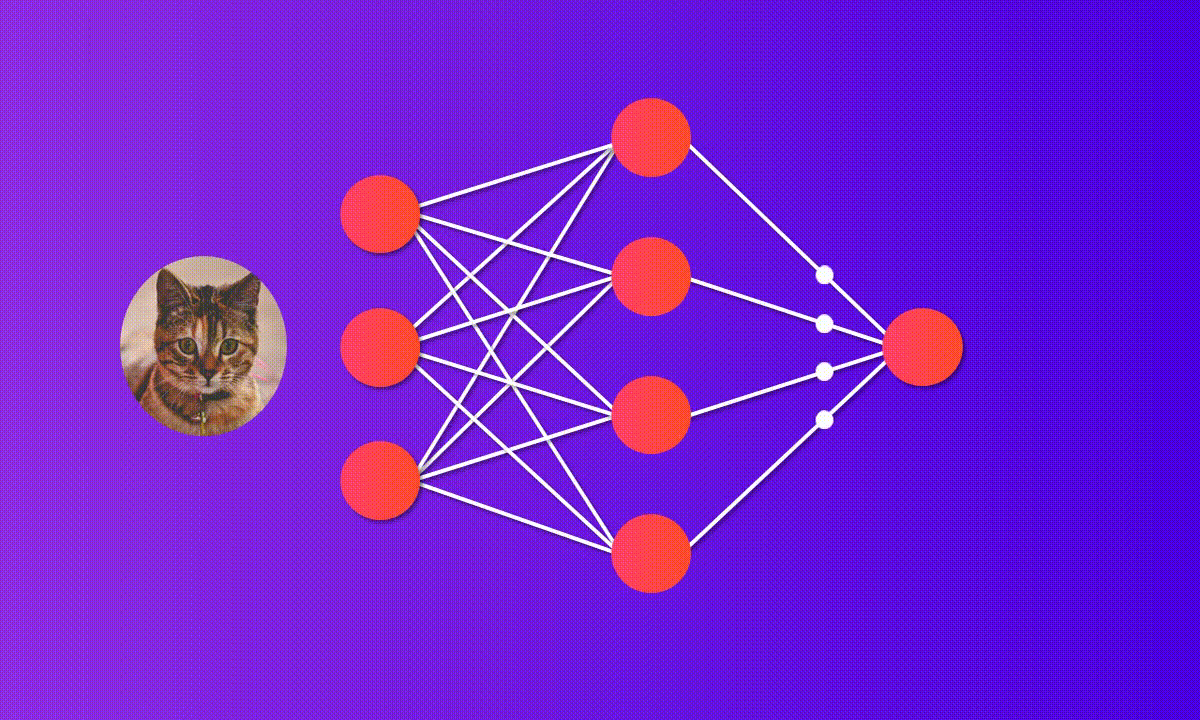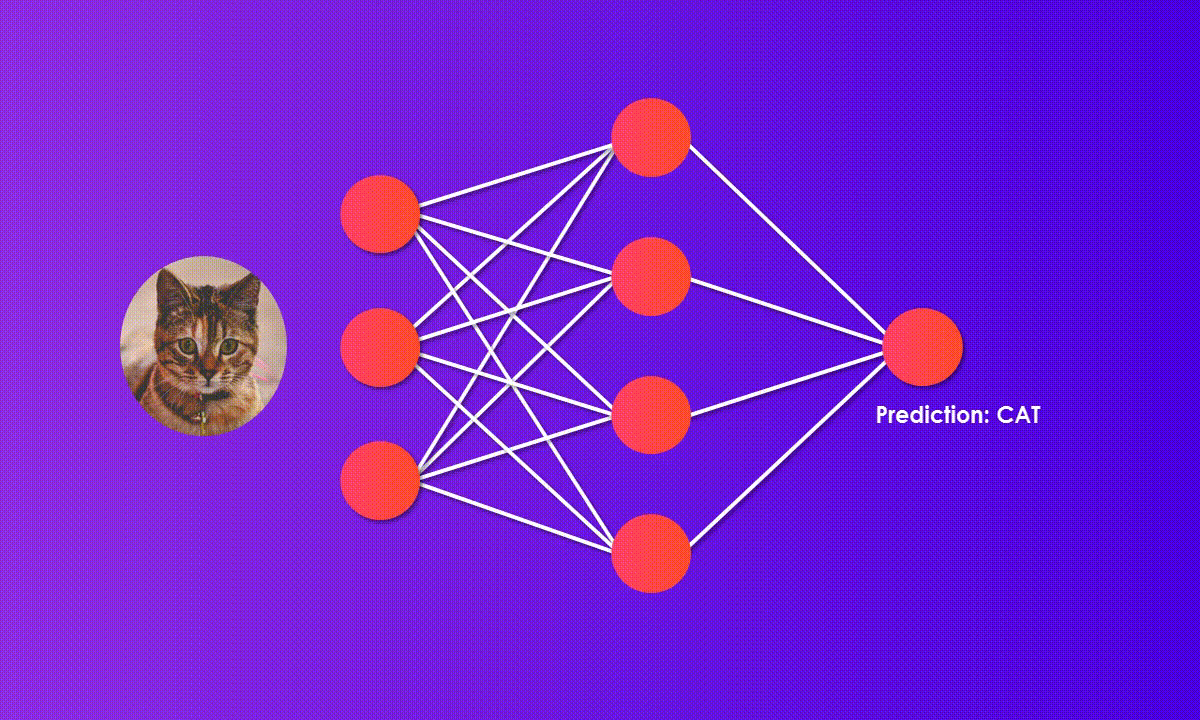
2012: AlexNet, CNN that won ImageNet competition
2014: GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks)
2015: AlphaGo beats professional Go player
2017: Transformer, Attention Is All You Need
The 2010s saw major breakthroughs with AlexNet winning the ImageNet competition, GANs creating realistic images, AlphaGo beating a Go champion, and the Transformer model improving language processing.
-
2020s - AI Creates and Converses
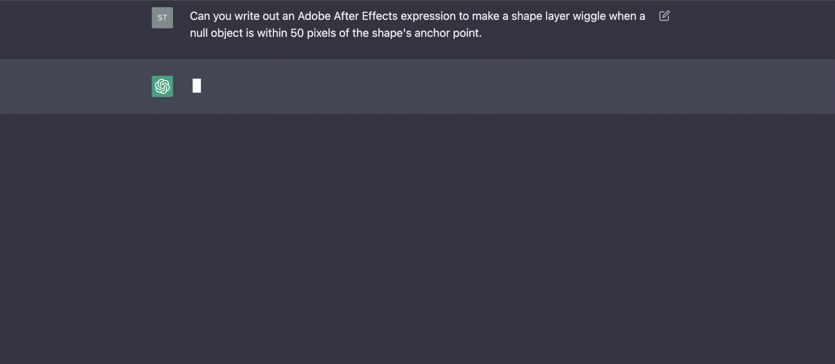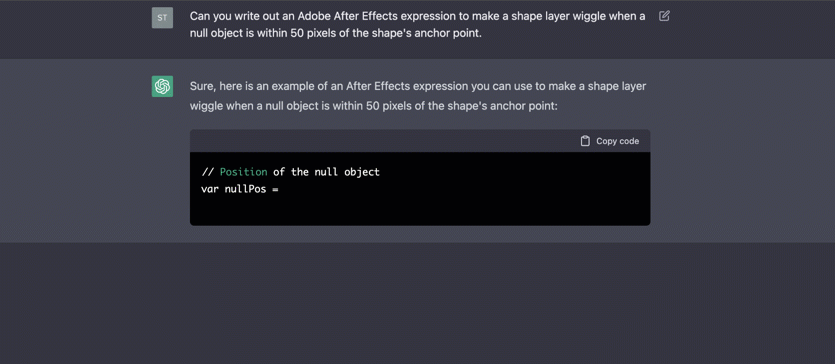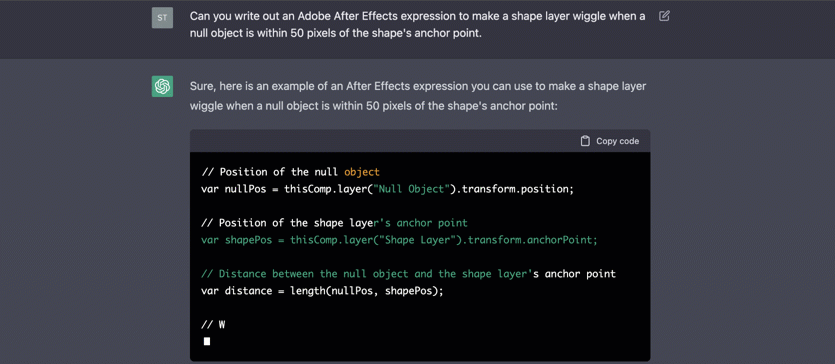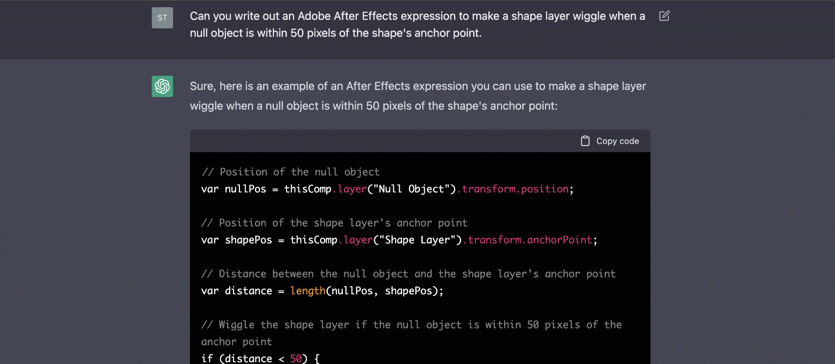
2020: GPT-3, large-scale language model by OpenAI - 7 grade IQ
2021: AlphaFold, protein folding AI by Google DeepMind
2022: DALL-E, image generation model by OpenAI
2023: ChatGPT, conversational AI by OpenAI - high school IQ
In the 2020s, AI has reached new heights with GPT-3 writing human-like text, AlphaFold solving advanced protein structures, DALL-E creating images from text, and ChatGPT having conversations like a human.